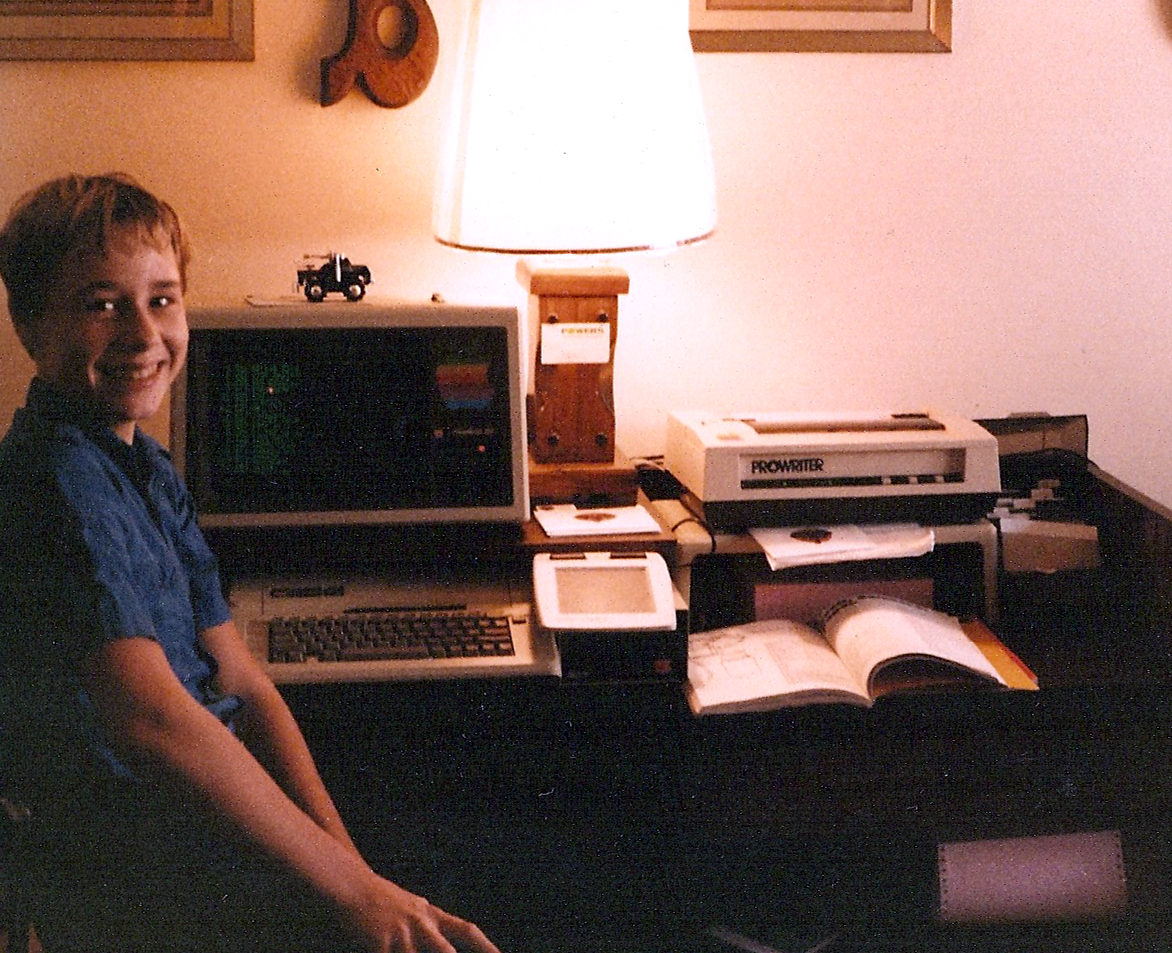
 Commentary before posting the article, I was a SysOp of a couple boards, I started a decade earlier than Lee, I started in the late 70's and, I recall when life upgraded to 300 bits per second (bps) from 110 bps and boy that was fast, not a dream of the speeds we suffer with today, I am right now connected at 16,150,000 bps and yesterday was announced speeds achieved 2,110,999,101,440,000,000 bps in the United Kingdom. To give you an idea, 8 bits in a character, so 110 bps would mean text would fill the screen at a rate of about 14 characters per second. My first was running on an Apple //e with a green screen monitor, the second was on PC and appeared in color like the screens below. Above is a photo with my Apple.
Commentary before posting the article, I was a SysOp of a couple boards, I started a decade earlier than Lee, I started in the late 70's and, I recall when life upgraded to 300 bits per second (bps) from 110 bps and boy that was fast, not a dream of the speeds we suffer with today, I am right now connected at 16,150,000 bps and yesterday was announced speeds achieved 2,110,999,101,440,000,000 bps in the United Kingdom. To give you an idea, 8 bits in a character, so 110 bps would mean text would fill the screen at a rate of about 14 characters per second. My first was running on an Apple //e with a green screen monitor, the second was on PC and appeared in color like the screens below. Above is a photo with my Apple.
Modems, wArEz, and ANSI art: Remembering BBS life at 2400bps
Here's how we geeked out in the era before the World Wide Web came to be.

Nerd hero Matthew Broderick uses his modem to actually attract a girl. This did not often happen in real life.
MGM/UA
You've almost certainly never seen the place where I grew up, and you never will because it's long gone, buried by progress and made unreachable by technological erosion and the fine grind of time. What I did and learned there shaped me, but that knowledge is archaic and useless—who today needs to know the Hayes AT command set, the true baud rates of most common connection speeds, or the inner secrets of TheDraw? I am a wizard whose time has passed—a brilliant steam engine mechanic standing agape in the engine room of the starship Enterprise.
I am a child of the BBS era. BBSs—that's "Bulletin Board Systems"—were sort of the precursors to the modern Internet, though that's not quite accurate, since the Internet evolved separately and in parallel. It would be more accurate to say that many people in their 30s and older today were introduced to the world of the Internet either through or because of the interlinked telephone universe of BBSs. That one experience begat the other.
 The author near the twilight of his BBS days. Notice the lack of girl, in contrast to Matthew Broderick above.
The author near the twilight of his BBS days. Notice the lack of girl, in contrast to Matthew Broderick above.
BBSs existed in a world that had yet to be soiled by smartphones and Facebook and Instagram; there was no Google, and indeed no World Wide Web at all. Up until 1992, the Internet was a thing primarily of text, and BBSs in many ways mimicked that. To get "online" was to sit down at your computer, open up an application called a "terminal program" (or just "term program" for short), pull up your carefully hoarded list of BBS phone numbers, and start dialing. Inevitably, most would be busy and you'd have to wait, but eventually you'd be treated to the sweet sound of ringing through your modem's speaker, followed by the electronic beeping and scratching of a modem handshake.
Oh, there were multi-line BBSs which could host more than one user at a time, but I didn't spend much time at those—the truly popular ones almost invariably required membership fees to support the cost of so many phone lines. No, most BBSs consisted of a single computer at someone's house, connected to a single phone line, which users dialed into one at a time. That remote computer was typically dedicated to the BBS because in the 1980s and early 1990s, multitasking operating systems like we have today were less common and much more temperamental. So, one at a time, users would dial into the BBS, check their private messages, perhaps leave a message on the BBS' "wall" for later callers, read and leave public messages in the message boards (called "subboards" or just "subs"), download and upload files, and then log off. If a modern Web-based forum is a crowded dinner party full of guests all yammering at the same time, a BBS was an entire house that you had all to yourself—one where you could enter, spend some time relaxing and reading books in solitude, write some letters, and maybe rearrange the furniture a bit.
The one who was
I was 12 years old in the fall of 1990, full of bespectacled junior high awkwardness and hunting, as all preteens are, for identity. At the time, my father worked for a big savings and loan firm, and in order to be able to occasionally do some work from our home PC, he was loaned a Hayes Smartmodem—a heavy external box that connected to our Acer 286/12 desktop via a thick RS-232 cable. I truly don't know if my dad ever used the device for work, but once the thing was plugged in, my world changed.
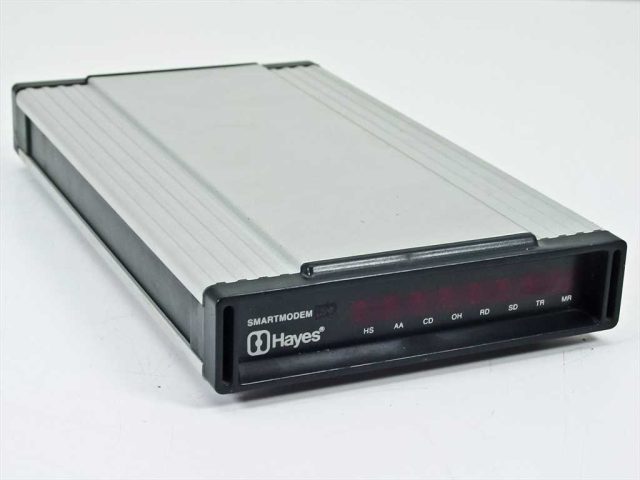

Enlarge / Chunky, heavy, and awesome: the Hayes Smartmodem 2400.
It came with some janky business-oriented communications application—likely Bitcom, but it was a long, long time ago and I don't remember the exact name—which was preprogrammed with a big list of (useless, to me) access numbers for business services. Seeing how interested I was in the device, my dad got the IT folks at his job to write down a few local BBS numbers for me to dial into.
The first BBSs I called, courtesy of that list, were hosted on Commodore computers running theSpiceWare BBS hosting software. If you happened to be using a Commodore computer with asemigraphical term program, it was a colorful and sound-filled experience (there's a video on the linked blog post of what a SpiceWare BBS looked like). For me on my IBM-compatible PC without even ANSI graphics, all I remember is a lot of red text.
I didn't care. It was absolutely incredible. It was like the computer in front of me had gained another dimension—it had become TARDIS-like, suddenly containing far more than its physical dimensions seemed to be able to allow. My computer could talk to other computers, and it felt like the boundaries of the world had just been blown out, like a cardboard box stuffed with dynamite. After I registered for an account on that first BBS, the remote system's menu showed me cryptic but exciting things I could do. Post messages? Download files? Play door games? Chat with the sysop? What's a sysop?
Learning the lingo
When it came down to it, there were three major activities one could do on a BBS: read and post messages, upload and download files, and play games. I quickly came to realize that me being on an IBM-compatible system meant that the files on these Commodore-hosted BBSs were useless to me, but I immediately fell in love with the message subboards. People were talking to each other! Inside the computer! And I could talk to them! And they would sometimes talk back!
These weren't multi-line BBSs, though, so the communication was very much serial. You'd call in, check your private messages to see if anyone had left you any, maybe take a peek at the public "wall" to see if anyone had scrawled anything funny, then flip over to the subboard of your choice and check for new posts there. For me, this was all done in text, though for Commodore users there were colors, semigraphics, and even sounds.
A "sysop," I quickly found out, was short for "system operator"—the person who ran the BBS. The sysop had administrative power and could do anything. On some BBSs they were jovial benefactors; on others, they were message-editing, power-abusing tyrants.
"Door games" were games that could be played through the BBS's text interface. They ranged from simple things (like maybe a Blackjack game) to deep, rich, complex simulations like Tradewars 2002. They were called "door" games because they were usually self-contained external applications, and the BBS application accessed them through an interface colloquially called a "door."
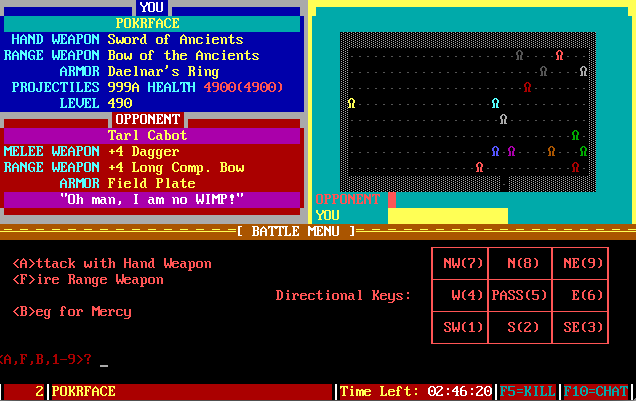
The Pit, a BBS door game. In this shot, I'm attacking these guys. Or maybe they're attacking me.
For most BBSs, the message subboards were the main reason people called in, and many BBSs tried to keep users active in those boards by enforcing a "PCR"—that is, a "post/call ratio." Users who wanted to download files had to post a certain number of messages in the subboards to keep their PCR up in order to be given access to the files areas. This often backfired, with some people posting useless "Post to get my PCR up!" type messages. On the other hand, you didn't want people hogging the board up, so users could only call in for a limited amount of time each day—often an hour. You could also bank your extra, unused time, sort of like rollover minutes. If you were done with a board for the day after only 20 minutes, you could stuff the other 40 into your time bank and use it later.
And the files—oh, the files. Once I started calling IBM-PC boards instead of Commodore-hosted boards, the files sections started to get more and more interesting. BBSs had different kinds of files depending on what the sysop wanted to do with his or her BBS; some boards had lots of programs to download and run, like screensavers or graphical demos, while some focused on amassing and distributing tremendous libraries of text files. It was rare to find a board without an ASCII copy of The Anarchist's Cookbook; the Cult of the Dead Cow or SubGenius texts were also heavily traded.
There were three other things you might see in a BBS's file area as well, and they were all weirdly linked together—ANSI art, MOD files, and warez. But before I could find out about any of those things, I had to escape from Commodore BBSs and start dialing into PC-run boards.
Speed—or lack thereof
But before that, we need to take a moment and put all of this modem stuff in perspective because you can't understand what it was like back then without understanding exactly how slow 2400bps is. We are accustomed these days to rich webpages and files delivered to us over always-on multi-megabit-per-second Internet connections, but that was the stuff of universities and governments back then. To put 2400bps in some perspective, that's 2.4Kbps, meaning that the last generation of 56Kbps modems were about 23x faster than poor old 2400bps. And everyone knows how "slow" 56K was.
At 2400bps and typical encoding, a single character took 10 bits of transmission (a start bit, a stop bit, and eight bits for the character itself, though other encodings were also used), and so the character rate maxed out at 240 characters per second. This was slow enough that you could actually see the screen fill with text, line by line. At 1200bps, fast readers could find themselves waiting on the remote computer; at 300bps (rare but not unheard of in the early 90s), fast typists could at times out-type their connection speed.
For text, 2400bps was perfectly adequate, but downloading binary files—images, large text files, compressed binary files, whole applications spread across floppy-sized disk images—took a long time. Exactly how long? The general rules of thumb to quickly estimate how long your download would take at 2400bps were that 1KB took about five seconds; 100KB took about eight minutes; and 1MB took about an hour and a half.
For someone who's never used a BBS—or for someone who's never had anything other than a broadband connection—it's hard to really explain just how different that is from today. Even downloading a single 256-color GIF usually meant several minutes of waiting, and a large multi-megabyte download was almost always an overnight commitment. There were a few ways to eke out more speed from your download—some download protocols like Puma and Lynx played games with the packets and sent them in batches rather than waiting for acknowledgments, and a few even used compression—but for the most part, you simply put up with it. Or you shelled out hundreds of dollars for a faster modem—not an option for my broke junior high self.
How bad was it then compared to how fast things are now? About this bad:
| DOWNLOAD SIZE & SPEED | 2400BPS | 9600BPS | 10MBPS CABLE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1KB: | 5 seconds | 1 second | Instant |
| 10KB (a text file): | About a minute | About 10 seconds | Instant |
| 50KB (a single .gif): | About 4 minutes | About a minute | Instant |
| 200KB (a large .gif): | About 15 minutes | About 3 minutes | Instant |
| 836KB (Wolfenstein 3D shareware): | About an hour | About 15 minutes | Instant |
| 2393KB (Doom shareware): | About 3 hours | About 80 minutes | About 1 second |
| 100MB (your whole hard drive): | About a week | About a day | About 80 seconds |
The comparison is so unbalanced it's almost meaningless, and it's the last line that puts it over the cliff of ludicrousness—a modern broadband connection matches and in some cases exceeds the bandwidth available to an early 1990s hard disk drive (the comparison becomes even more insane at 50 or 100 Mbps).
How could we possibly stand it without rioting? The answer is simple: you can't miss what you've never had before. 2400bps was as fast as most of us had—most of us who weren't rich or actively distributing warez, anyway—so 2400bps was what we used. It was slow, but it was simply the way things were.
Term programs, World War IV, and the golden age
I acquired more BBS numbers from each board's public phone list, and I quickly found out that when calling into PC BBS systems, I needed something far more powerful than the default terminal program. There were many choices, but everyone I talked to recommended something called ProComm Plus, which massively improved on my default program by offering things like an extensible phone book and the ability to display ANSI "graphics"—colored text and extended characters that could be strung together to make rudimentary images.
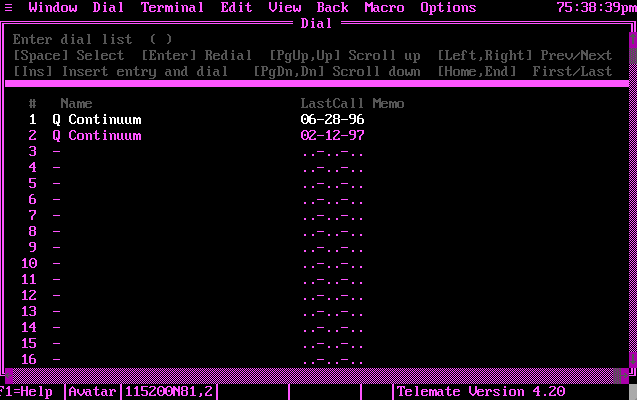
Telemate's dialer screen. I was incredibly excited to see that the copy of Telemate I had sitting in my archive directory was my actual old version, complete with the last two Houston BBSs I used to call (and my actual last two connection times!). Also, Telemate apparently isn't Y2K-compliant, because it thinks it's 75 o'clock.
However, the term program I used more than anything else was the venerable Telemate, by White River Software. Telemate had it all: it was a multi-threaded application and could actually do a lot of neat things simultaneously. It had a configurable "back buffer" so that you could go back and look at things that had scrolled off your screen (remember, this was MS-DOS—cut-and-paste and scrolling were both a big, big deal), a text edit window you could open and close, functional cutting and pasting, and a rich macro language that could be used to do things like automatically enter your username and password on certain BBSs. It also had a powerful, extensible dialing list—great for automatically finding that one BBS without a busy signal on a Sunday afternoon.
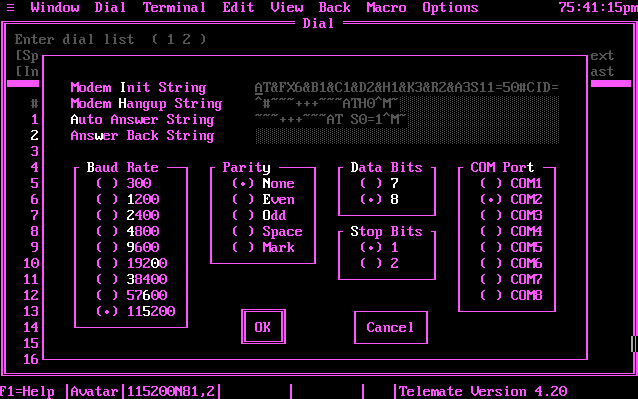
Configuring Telemate's main comm options. Note that awesome extended init string! At the time I was rocking a USR Courier V.Everything, so I had all kinds of extra registers to control.
Just as there were different terminal programs for users, there also was a plethora of BBS host applications, too. Different areas of the country tended to have different BBS applications that dominated; here in the Houston area, most of the boards I ended up frequenting for many years used a program called TAG (properly styled "TAG!"), which shared many similarities with the vastly popular WWIV BBS application (which in turn had spawned other similar-looking BBS applications likeTelegard and Renegade).
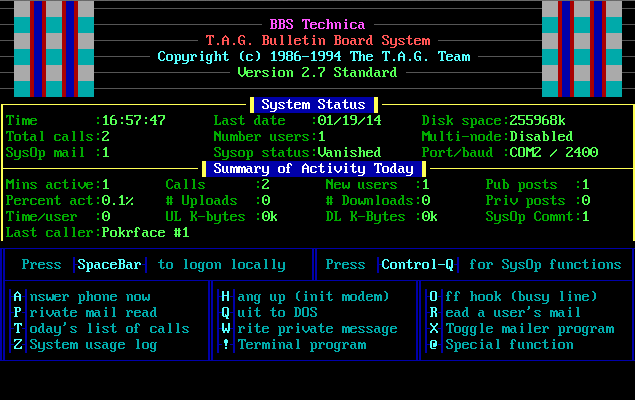
The secret magic screen TAG sysops stared at while waiting for someone to call.
Although TAG was by no means the only BBS application in general use around Houston, the majority of the BBSs I called into in the 1990s used it. When I think of furtively downloading a pirated version of DOOM, in my head I see the TAG download interface. When I think of those very first arguments I ever had about Macs versus PCs or who the superior captain of the Enterprise was, it's in the ANSI colors of the TAG message board composition window.
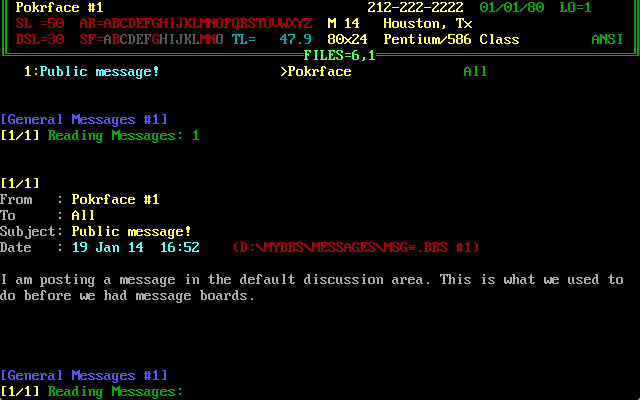
Posting and reading messages on a BBS looked pretty much like this.
That was truly the prime draw of it all—all that talking and arguing with fellow geeks. Through the computer, we were all democratized—we transcended social stigmas and the crushing weight of the high school popularity pecking order. Our voices mattered—to each other anyway. On the whole, no one really cares about a bunch of geeks talking about geek things, but to us, the reality of owning a medium was profoundly empowering. No one was going to make fun of anyone for arguing over whether attack matrices were a superior system to THAC0. Your viewpoint might be mocked, but not the fact that you were having the conversation. Not as long as you were posting in the appropriate sub.
Each BBS was an island (relay mail between BBSs was a thing, but I rarely used it), and each board included its own cliques and pecking order. A sysop on one board might be a "co-sysop" on another (effectively an assistant system administrator with most of the sysop's powers—banning users, reading other users' private messages, and so on). Or he might not be—just because you had your own BBS didn't automatically give you any rights on someone else's board. Particularly trusted users might be made "subops" of particular discussion subboards, granted powers much like a forum moderator of today. To be a subop or a co-sysop was a mark of high status, and it was pretty common for folks to try to beg and wheedle their way into those roles merely to hold it over other users.
Long distance fees kept most BBS users confined to their local area codes; I stayed local for fear of invoking my parents' wrath (and, later, when I started paying for my own phone line, I was even less inclined to call a board outside my area code). You'd see the same nicknames pop up over and over again on different boards—it was common for a user you knew on one board to appear on another, too, since there were at most a hundred or so really popular local BBSs at any given time. In-jokes flourished in our semi-closed ecosystem, and things felt downright cozy.
Of course, there was a whole world outside of the 713 area code. Game manufacturers in particular had BBSs that glittered like jewels, just outside of my reach, promising hints and mysterious fixes—"patches," they called them. Once, after begging and begging, I was given permission by my parents to dial into Sierra's BBS so that I could download a patch to fix a game-breaking bug in Quest for Glory 4. Calling that faraway BBS felt a little bit like making a holy pilgrimage—after playing Sierra's games for so many years, I was going to actually talk to their computers! (The patch ended up fixing the issue but also made it impossible to reload any of my saved games. I never finishedQFG4.)
I learned things in this world, things that teenagers these days have to pick up from the infinite multitude of Web-based discussion boards and social media. Back then we didn't have to worry so much about our parents finding our smartphones and our snapchats and our Facebook posts, though, because barriers to entry were higher. Our world was cloaked not just in passwords, but in incantations and ASCII arcana. Even dialing into a BBS required a bit of understanding of how the term program you were using worked. Without some idea of what you wanted to accomplish, it would have been difficult to puzzle out how to do it.
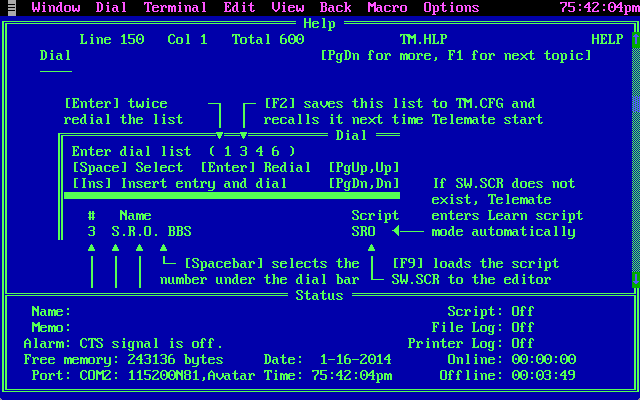
Can't figure out your terminal program? No worries! Here's your help screen! ALL BETTER NOW, RIGHT?
Xmodem! Ymodem! Zmodem!
Even downloading files—something that today is done almost without thought by clicking links on a webpage—took some thought and know-how. You didn't just "download" something from a BBS, you had to actually tell your terminal program that the data it was about to receive was a file and not text to display. This meant configuring and using a download protocol. The three most common protocolswere Xmodem, Ymodem, and the sophisticated and widely used Zmodem; each of them let you download files, but Zmodem was far and away the easiest to use.
Poor old Xmodem didn't know anything about what you were downloading. You'd pick a file from the remote BBS to download, but then you had to hit the "download" key in your term program, select the Xmodem protocol, supply a file name to save the download as, and wait. The remote computer didn't transmit anything except data—no error correction, no size, no time remaining, nothing. Ymodem introduced a bit of error correction, but it wasn't much better.
Zmodem, on the other hand, was the protocol of kings. It was fast—it streamed rather than requiring an acknowledgment after each packet. It was smart, too—it even let you restart aborted downloads, which was a huge bonus when each megabyte downloaded represented almost 90 minutes of real time, and a large interrupted download could mean a whole day wasted.
Other more exotic protocols were around too if you wanted to download their binaries to set them up (and if the BBS you were calling supported them). Of particular note was Hilgraeve Software'sHyperProtocol, a streaming protocol which included a bit of compression. You might not ever have used it, but anyone who worked in IT has almost certainly used the terminal emulator Hilgraeve produced a few years later: HyperTerminal.
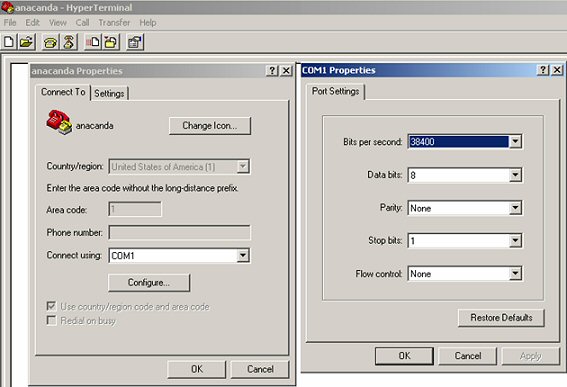
Remember this thing? It's got a surprisingly complex history.
MOOOOM, DON’T PICK UP THE PHONE!
In a time when my family only had a single landline, time on BBSs had to be carefully negotiated. Every moment I was living in that world was a moment where the phone was off-hook and no one could call our house. Relatives began to complain about always getting a busy signal when they dialed us, and I received more than one talking-to from my parents about always being on the phone. In that respect, I suppose I was like most teenagers.
Modems work by encoding digital information into an analog signal, and most people have heard the static-y "HISSSSSSS" of modem communication. Noise was data, and extraneous noise in a connection between two modems—noise from a bad connection, or noise introduced by someone's mother picking up the phone—caused errors. As modems grew more sophisticated, error correction techniques like MNP and V.42bis began to appear on consumer-priced modems, but when I first began dialing into BBSs, error correction wasn't common on 2400bps modems that normal people could afford.
Minor bouts of line noise looked like random characters injected into the flow of things—annoying, but easily fixable. However, sometimes a relative innocently picking up the phone while you were online would cause your connection to drop, which could be terribly frustrating if you had managed to dial in to a popular BBS that was normally busy.
Our family's computer was located in an add-on room to the house, and that room had no phone jack. For years, I stretched a 50' (about 15 meter) phone cord across half the house in order to get online. This meant that connections were spoiled not only by the occasional picking up of a phone, but also by the occasional tripping over the cord. One of the first things I did when I turned 16 and got a jobwas pay for the installation of my own phone line and a jack in the computer room. It cost me about $50 a month for a number that could call most of Houston (a 332 exchange number rather than the cheaper 554 exchange), and back then I actually spent more on my phone line's monthly bill than I did on gas for my blue 280-Z.
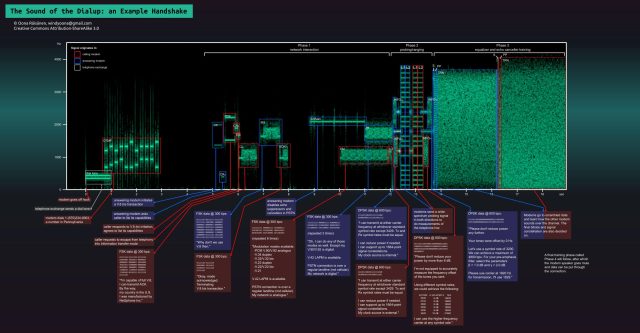
Enlarge / A high speed (V.90 or V.92) modem handshake, annotated. 2400bps handshakes were much less complex.
Oona Räisänen
Talking to your modem
Regular BBS users became skilled in the Hayes AT command set—the language for configuring and using the majority of modems. Term programs hid a lot of the complexity by automating the process of dialing and using a modem, but to tweak the modem's parameters it was necessary to dive in and start directly changing settings. That meant using AT commands.
When you first started up your term program, it passed a long bunch of commands called the "initialization string," or just "init string" to your modem. This set parameters in the modem's nonvolatile RAM so that the modem would function in the way you expected or wanted. Though my init strings got more complex as I got newer and newer modems, I'll forever remember the string I used with my beloved old Hayes 2400 Smartmodem:
ATE1S7=255S11=35V1X4S0=0
All commands started with "AT," for "attention," to tell the modem it should expect commands. E1 set local echo on (so that I could see what I was typing in the term program's main view). Then the command set several "S registers"—NVRAM locations that held specific settings. "S7=255" set the number of seconds after going off-hook that the modem would wait for a connection to 255. "S11=55" set the DTMF tone length to 35 milliseconds—so when the modem dialed, it would use 35 ms for the length of each dialed digit (shorter DTMF tones meant faster dialing—through experimentation, I found 35 to be the shortest that would work with my local POTS exchange). "V1" told the modem to give me result codes in plain English rather than as numbers (so it would print "BUSY" in the terminal window if it detected a busy signal rather than just printing a number), and "X4" told the modem that it should use as many result codes as it knew how to use—in other words, it should be as smart as possible and respond to dial tones and busy signals rather than blithely dialing away. Finally, "S0=0" set the auto-answer register to 0; setting "S0=1" would cause the modem to automatically pick up the line after the first ring if it heard an incoming call. That would be great if I were running a BBS, but not so great on a line used primarily for voice.
You could also send commands directly to the modem. The most useful was "ATA," which you could type at any point to cause the modem to pick up the line and start trying to connect—great if a friend was going to call to upload a file directly to you. Also useful was quickly typing "+++ATH0"—the "+++" would pull the modem out of data mode and into command mode when you were connected, and "ATH0" would cause the modem to instantly hang up.
Online gaming
We played games in that lost world, too, and some of them were amazing. I spent more time than I care to admit playing The Pit, an arena fighting game where you move your little ASCII character around in an ASCII arena and fight other ASCII characters for loot and fame. I would bank all my excess time on BBSs throughout the week, then make huge time bank withdrawals on the weekends so that I could tie up phone lines for hours bashing imaginary text-mode monsters.
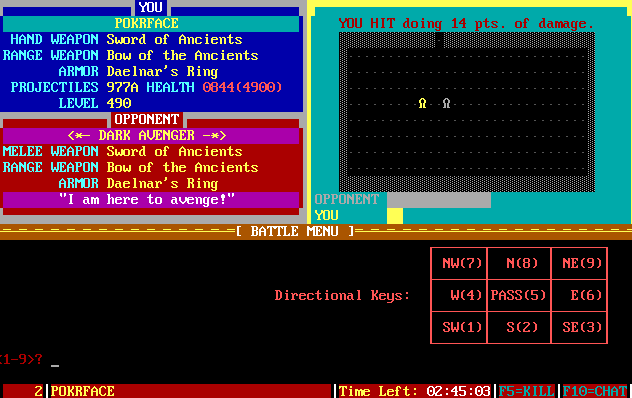
More of The Pit. I might be in a little bit over my head here.
One of the most long-lived and popular door games was TradeWars 2002. TW2002 dropped players into a large persistent universe and gave them a certain number of turns per day to trade, explore, fight, and get rich. It was sort of like a cross between Elite and Galactic Civilization, though the multiplayer competitive aspect of it was absolutely entrancing.
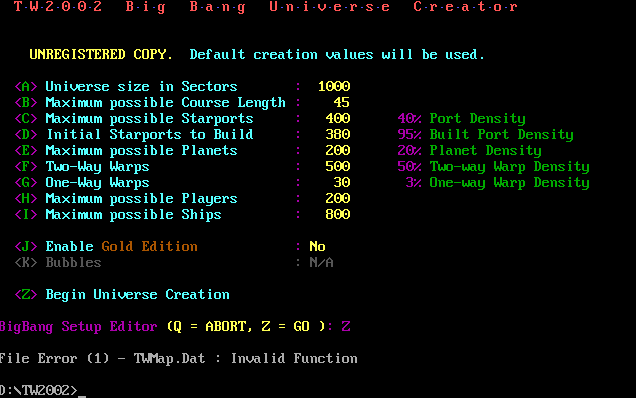
I tried to set up Tradewars 2002 in DOSBox so I could take some pictures, but I couldn't make it work. However, the game pretty much looked just like this anyway.
That multiplayer, though, was "serial" instead of parallel. Most BBSs were single-line, so the game was much more like a huge multi-sided game of chess rather than a modern MMORPG. And that persistent TW2002 universe was really only persistent on single BBSs—your TW2002 game on one board was a different game from your TW2002 game on another board (because, remember, few BBSs were connected together). These were most often single computers being run by a sysop out of his or her house with a single phone line. (Although TW2002 itself did support multi-line BBSs for simultaneous play and even multi-BBS play via relay for sysops who wanted a universe that spanned boards.)
A pirate’s life for me?
And, of course, there was pirated software—which even back then was called "warez" (pronounced like "wares," not like "Juarez"), though it was the style in the mid-'90s to soMeTiMeS wRiTe iT liKe "wArEz." I can't believe I used to write like that, but we all did for a while.

Pirated file areas were sort of like secret bars in the 1920s—everyone knew where they were, but you didn't really talk about them in public. Saying "HEY GUYS ANYONE GOT ANY WAREZ" on a BBS' message boards might get you immediately kicked and blacklisted; quietly approaching the sysop in chat and mentioning that you heard from another board user that there were "private" files for download, on the other hand, might get you access—provided someone could vouch for you.
Through BBSs, I came to know the world of pirate release groups—the Scene. As I downloaded applications I wanted to use but could never pay for (like the incredible, inimitable XTree Gold) I quickly became familiar with the legendary names: groups like iNC, THG, Fairlight, and the still active seemingly immortal RAZOR 1911. These were the people actively cracking software and distributing it, and they were mythical creatures in my teenage eyes.

Pirated software in the BBS days was very different from its modern times' equivalent. Grandparents tell stories of how back when they were young, they didn't even have to lock the doors of their houses because crime was so low, and that same golden-age recollection applies here. You simply didn't have to worry about viruses from a scene release. The cracking groups all competed viciously for reputation and popularity, and no one would sign their name to a release tainted by a virus. They put out clean software, and like hippies at Woodstock, we rarely worried about viruses or protection.
Intros, cracktros, and ANSI art galore
Oddly, the pirated software scene and the digital art and music scene were closely intertwined. BBSs were primarily a textual medium, but "text" can mean many things beyond the alphabet and basic punctuation. Skilled artists existed who could take extended ANSI characters and colors and create not just recognizable artwork, but legitimately amazing images.
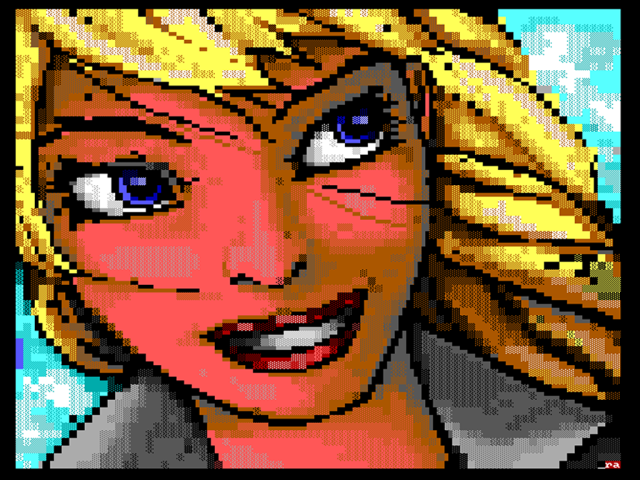

Enlarge / "Ansi Blondie," by Reanimator of iCE. This is all made out of colored ASCII characters.
Many of these artists were also either tied to or directly members of big cracking groups, and their services were very much in demand. A piece of pirated software would always have a file in it that contained information about the release, including who released it; those files would typically have embedded ASCII or ANSI art in them. Further, the BBSs where cracking groups directly communicated and hung out needed to be decorated, and these often featured incredibly elaborate logon screens and backgrounds.
ANSI art remained intertwined with the cracking scene, but it also evolved its own elaborate scene, with its own conventions and stars. Art groups like ACiD and iCE flourished in the 1990s, releasing incredible art often made out of nothing more than colored characters.
The mass of skilled coders and artists did far more than simply crack software and make images taunting rival groups; it became popular for pirate groups to include musical and graphical "intros" alongside their releases. An "intro" (or "cracktro," since the intro would often accompany a cracked piece of software) was a small self-contained musical calling card—typically, it would be a set of stills or animated images with a 4-channel digital audio song (like a .MOD) playing in the background. There would almost always be a list of "greets" in the intro, where the coders shouted out praise to their friends and talked smack about rival groups.
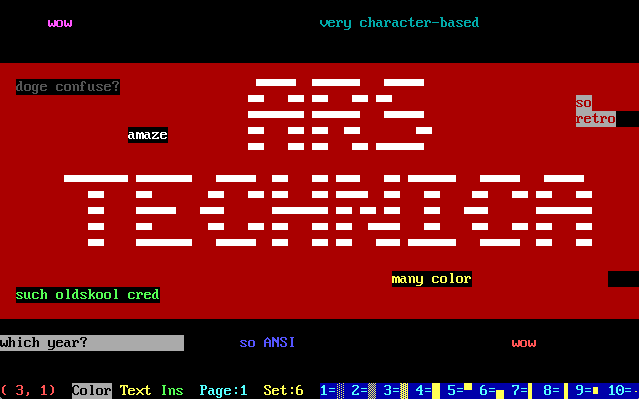
I fired up TheDraw to make some bitchin' ANSI art myself, but discovered that I cannot art any better today than I could back then. So, this is the best I can do—going for kind of an ironic statement, I think.
Intros moved beyond simple calling cards and evolved into massive applications designed to push computers of the day to their limits, and many of the players that started out in the demoscene are still active today in one form or another. For example, Future Crew, creators of arguably the two most famous demos of all time (Unreal and the mind-blowing Second Reality) are still coding—you might recognize their work at Remedy Entertainment and FutureMark.
Speeding up—9600, 14400, and beyond
In early 1994, after years and years of 2400bps, my dad bought me a high-speed modem. I graduated to 9600bps. At that time, the fastest thing you could buy was a USRobotics HST modem, which operated at 16800bps using USR's proprietary HST communications scheme. After that, 14400bps was widely popular and became what the elite used.
I was thrilled to have my 9600bps modem, though, since it represented a five-fold increase in speed over poor old 2400bps. I still remember the absolute joy of watching my download rate jump to 1KB per second—it was magical, watching those numbers tick away so quickly. I could download 100KB in a little over a minute and a half! A megabyte in a bit over 15 minutes! I could download anything.
Of course, all that speed led to me downloading a lot more stuff—mainly pirated software and music. By that point, our 286/12 had long been replaced—we got a 386/25 with a Soundblaster Pro—and I fell headlong into the world of .mod files and more complex digital audio files. I filled expensive hard drives with applications and music, trying to see and discover everything.
The end of all things
By the time I bought myself a 28800bps modem in 1996, my BBS use had faded to nothing thanks to a new and much more addictive thing: the Internet. Thanks to Netcom Netcruiser, I left behind my door games and file areas and quaint local subboards for the mid-'90s Internet, which was itself still a relatively young and wild thing (especially the nascent World Wide Web, which was at the time only a few years old).
 Sadly, this thing right here killed BBSs for me.
Sadly, this thing right here killed BBSs for me.
But even as my online world gained width and breadth, it lost a magical sense of depth. There are somany things to do on the modern Internet; even the Internet of 1995 and 1996 was a vast ocean of destinations and information. Gone, though, was the intimacy of the BBS—it was all fine and good to speak of visiting someone's homepage on the Web as a personal experience, but the ephemeral loading of a webpage is nothing in comparison to dialing into a BBS that a person has specially crafted for visitors. It's the difference between reading a billboard on the side of someone's home and actually entering that home to sit down for tea.
It seems crazy that the text-based world of BBSs could still resonate so much with me, but what I learned there underpins most of how I use the Internet today. I learned how to talk with other people in a forum, how to quote replies, and how to construct an argument. I learned how private messages work. I learned about compressed files and archives—would it surprise younger Internet users to learn that we used PKZip and ARJ back then, just as we do now? I learned how to flame someone and how to respond to being flamed. I learned about analog communication and modems and hard drives and how computers worked—I had to learn, because that was the only way to get "online" back then.
And I miss it. There was an innocence then that's absent now from the online world. You'd never see an ad on a BBS; you'd never get spam in your inbox or have to worry about your parents or your boss finding out about a picture you'd posted (because, really, "posting" that picture involved a whole hell of a lot of steps). You worried that "the government" might find out you downloaded a text file telling you how to build a blue or red box, but you didn't really worry about it.
What we have now is quantifiably better in just about every way... but you love the things you grew up with. Some BBSs are still around, though most are accessible via telnet, and that's just not the same. My generation is in a perfect spot to have experienced it in the mid-1990s—those older than I were in college at the time and were cutting their teeth on the actual for-real Internet, using USENET and FTPing files around with abandon. Those even a few years younger than I missed all of it and likely got their first introduction to a modem through nascent services like America Online or Prodigy.
They'll never know what it was like to prank-call friends' BBSs late at night, whistling into the receiver to trick the remote modem into trying to train against your whistle and lock up. They can't recall the thrill of discovering the full registered version of Wolfenstein 3D on a private board for the very first time or the joy in slaving over TheDraw for hours to produce the perfect ANSI signature to append to your messages.
Childhood ends for everyone, but I'm glad I spent mine online.
+++ATH0
!@^^§¡©£¡)
NO CARRIER
NO CARRIER
No comments:
Post a Comment